How Do Proximity Switches Work?
September 24, 2014 |

Proximity switches open or close an electrical circuit when they make contact with or come within a certain distance of an object. Proximity switches are most commonly used in manufacturing equipment, robotics, and security systems.
There are 4 basic types of proximity switches: infrared, acoustic, capacitive, and inductive.
Infrared Switches
These work by sending out beams of invisible infrared light. A photodetector on the proximity switch detects any reflections of this light. These reflections allow infrared proximity switches to determine whether there is an object nearby. As proximity switches with just a light source and photodiode are susceptible to false readings due to background light, more complex switches modulate the transmitted light at a specific frequency and have receivers that only respond to that frequency. Even more complex proximity sensors are able to use the light reflected from an object to compute its distance from the sensor.
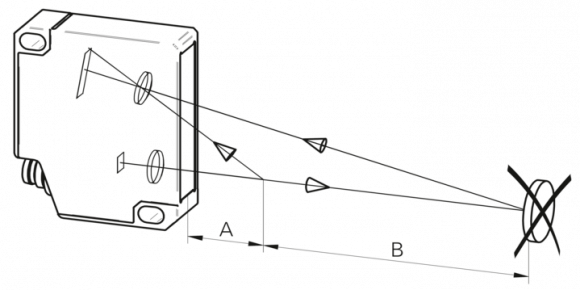
Courtesy of Baumer
Acoustic Switches
These sensors are similar in principle to infrared models, but use sound instead of light. They use a transducer to transmit inaudible sound waves at various frequencies in a preset sequence, then measure the length of time the sound takes to hit a nearby object and return to a second transducer on the switch. Essentially, acoustic proximity sensors measure the time it takes for sound pulses to “echo.” And they use this measurement to calculate distance, much like the sonar used in submarines.
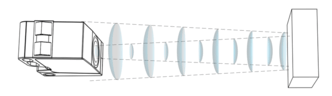
Courtesy of Baumer
Capacitive Switches
These switches sense distance to objects by detecting changes in electrical capacitance around it. A radio-frequency oscillator connects to a metal plate. When the plate nears an object, the radio frequency changes. Then, the frequency detector sends a signal telling the switch to open or close. These proximity switches have the disadvantage of being more sensitive to objects that conduct electricity than to objects that do not.
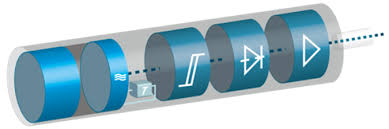
Courtesy of Baumer
Inductive Switches
These switches sense distances to objects by generating magnetic fields. They are similar in principle to metal detectors. A coil of wire is charged with electrical current, and an electronic circuit measures this current. If a metallic part gets close enough to the coil, the current will increase and the proximity switch will open or close accordingly. The chief disadvantage of inductive proximity switches is that they can only detect metallic objects.
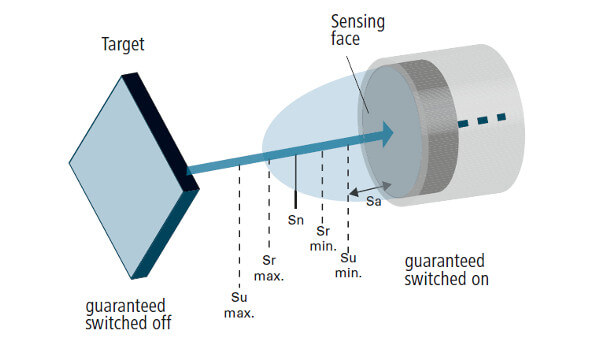
Courtesy of Baumer
Proximity Switches For All Your Needs
Proximity switches are used in many different manufacturing processes. Some examples include measuring the position of machine components, security systems, in applications such as detecting the opening of a door. Uses also include robotics where they can monitor a robot or its components’ nearness to objects and steer it accordingly.
If you need valves, sensors, or other pneumatic components, then get in touch with us! We’ll help you get the right parts for any of your needs.
